How to Update Firefox Browser?
Having played with browsers' settings to optimize performance and security, I ...

As someone who has explored countless browsers to optimize performance, I’ve often tackled the frustrating question: why is Firefox so slow?
Mozilla Firefox is one of the most popular web browsers because of its emphasis on privacy and personalization. Like all software programs, it will go through periods of slow operation where everyone will ask themselves, why it is so slow. This post outlines some of the common reasons behind slowdowns and actionable changes that can be made to improve the performance of Firefox.
One of the most attractive things that Firefox offers is its huge repository of extensions. However, too many add-ons or poorly optimized ones really take a toll on the browser’s speed. Extensions use up memory and CPU, which, when combined-especially when add-ons run scripts in the background-can make Firefox sluggish.
You may experience degraded performance if you are on an older version of Firefox. Most updates usually house performance enhancements and bug fixes, so keeping it un-updated automatically makes it slow.
With browsing, cached files and cookies build up over time. Meant to speed up the loading of websites, an overloaded cache does precisely the opposite. A bloated cache will slow down page loads and make Firefox less responsive.
Firefox can be resource-intensive, especially if you open a lot of tabs or run a low-end machine. It can be because the browser chokes due to low RAM or minimal CPU power.
Some advanced settings, such as hardware acceleration or proxy configurations, may inadvertently cause the slow operation of Firefox. The features were put in place for functionality and speed, but on some systems, they could do the opposite.
Regularly clearing your cache and cookies has often fixed problems that were being caused by outdated or corrupted data. To do so,
1. Click the hamburger menu in the top right and select Settings.
2. Select Privacy & Security in the left column. Then, in the Cookies and Site Data section, click on Clear Data.
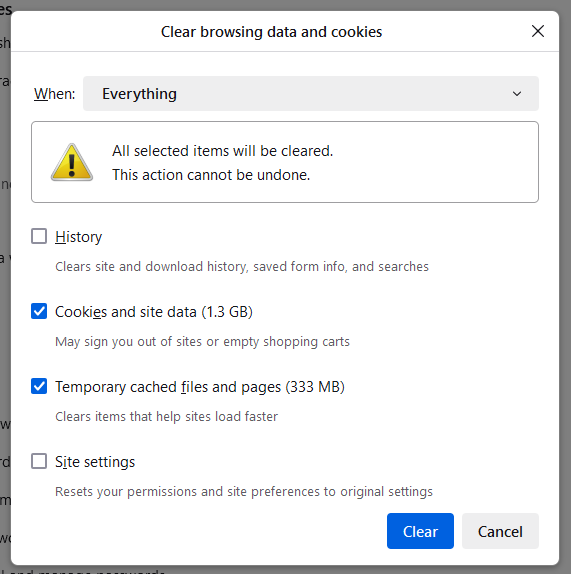
3. In the dropdown menu next to the expression “When”, select Everything. Then, check both Cookies and site data and Temporary cached files and pages. And finally click on Clear.
This simple step is quite often the solution to the question “why is Firefox so slow?”
1. For that, click the hamburger menu, then Add-ons and Themes.
2. Browse through the list of extensions and disable the ones not in use.
3. Leave enabled only really trusted and necessary extensions.
Always use the latest version of Firefox. Updates often have optimizations that handle bottlenecks in performance.
1. Click the hamburger menu, then select Help.
2. Go to About Firefox.
3. If an update is available it will automatically download and install.
There was a time when, out of frustration, I kept asking myself, “Why is Firefox so slow?” I used Firefox both for work and personally, opening a number of tabs that usually involved multiple projects. The more time went on, the more I experienced huge delays, like with tab switching and loading of pages.
Doing some digging, I found the culprit: too many extensions were enabled. I had downloaded dozens of add-ons, and I wasn’t even using a majority of them. For example, turning off the extensions that I did not really need, along with regular cleaning of the cache, returned Firefox to its previous speed. It was quite a simple solution, but it underlined very effectively how much the user’s surfing habits will affect browser performance.
Hardware acceleration is a technology where the performance of some tasks is transferred from the CPU to the GPU. This may result in increased performance but might be problematic for systems that are older or incompatible.
1. Open Settings > General > Performance.
2. Deselect “Use recommended performance settings.”
3. Toggle off “Use hardware acceleration when available.”
If Firefox remains slow, Refreshing Firefox resolves deeply set problems by restoring Firefox to its default state.
1. Click the menu and choose Help > More Troubleshooting Information.
2. Scroll down to the section marked “Give Firefox a Tune-Up” and click Refresh Firefox.
Advanced users can try increasing how many content processes the browser uses. To do so, increase the Content process limit (a higher value will improve multitasking but will use more RAM). Here’s a video that’ll show you how to do so:
It’s designed with privacy and customization in mind, sometimes at the cost of raw speed. Unlike browsers like Google Chrome, which optimize heavily for performance at the cost of data collection, Firefox places a much greater emphasis on respecting user privacy and offering more granular control.
Finally, Firefox’s architecture has a focus on web standards and open-source collaboration; at times, it just feels slower because of those facts compared to proprietary browsers designed for speed-first functionality.
1. Why does Firefox feel so much slower than Chrome?
Firefox might feel slower than Chrome because of the fact that it focuses more on privacy and configurability than just plain speed. Besides, the heavy optimization of Chrome regarding Google services gives them an advantage in many situations.
2. How do I speed up Firefox?
You can speed up Firefox by disabling superfluous add-ons, cleaning your cache and cookies, updating the browser to its latest version, and fiddling with settings like Hardware acceleration.
3. Does Firefox use more RAM as compared to other browsers?
Firefox has greatly improved the way it uses memory, but when a user opens a lot of tabs or uses several heavyweight extensions, it sure does suck up quite a lot of RAM.
4. Is hardware acceleration necessary in Firefox?
Hardware acceleration can improve performance in newer systems, but slows down an older device. You can try turning off hardware acceleration if you encounter any issues.
5. Why is Firefox slow to open tabs?
Slowness will occur when there are limited system resources, many resource-intensive add-ons, or when an older version of Firefox is in use.
6. How often do I need to clear my cache in Firefox?
Every couple of weeks is a good idea, or when your performance goes bad.
7. Can I fix the slowness just by reinstalling Firefox?
Yeah, you can, since uninstalling and reinstalling bring a fresh installation for the browser with no old data or corrupted files.
8. Does Firefox’s focus on privacy make it slower?
Quite somewhat. Perhaps the privacy-first approach means Firefox really focuses its efforts on user protections rather than on optimizations for raw performance.
If you’ve been asking yourself “why is Firefox so slow,” rest assured that there are plenty of solutions to address the issue. From managing extensions to optimizing settings and clearing your cache, small changes can make a big difference in Firefox’s speed.
Firefox may not compete on raw speed with the other browsers most of the time, but it certainly makes up for lost ground with its huge ideas on privacy, transparency, and customization in order to keep reliably consistent for users who take control of their online world. Knowing what causes slowness, and proactive steps are indispensable for a smooth, speedy browsing on Firefox.
Leave A Reply